
A practical framework for environmental governance (Bennett & Satterfield, 2018)


A practical framework for environmental governance (Bennett & Satterfield, 2018)
I just published a new paper in Marine Policy titled “Navigating a just and inclusive path towards sustainable oceans” (link to paper). This agenda setting paper argues that the ocean science, practitioner, governance and funding communities need to pay greater attention to justice and inclusion across key ocean policy realms including marine conservation, fisheries management, marine spatial planning, the blue economy, climate adaptation and global ocean governance.
Reference: N.J. Bennett, Navigating a just and inclusive path towards sustainable oceans, Marine Policy. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2018.06.001
Abstract: The ocean is the next frontier for many conservation and development activities. Growth in marine protected areas, fisheries management, the blue economy, and marine spatial planning initiatives are occurring both within and beyond national jurisdictions. This mounting activity has coincided with increasing concerns about sustainability and international attention to ocean governance. Yet, despite growing concerns about exclusionary decision-making processes and social injustices, there remains inadequate attention to issues of social justice and inclusion in ocean science, management, governance and funding. In a rapidly changing and progressively busier ocean, we need to learn from past mistakes and identify ways to navigate a just and inclusive path towards sustainability. Proactive attention to inclusive decision-making and social justice is needed across key ocean policy realms including marine conservation, fisheries management, marine spatial planning, the blue economy, climate adaptation and global ocean governance for both ethical and instrumental reasons. This discussion paper aims to stimulate greater engagement with these critical topics. It is a call to action for ocean-focused researchers, policy-makers, managers, practitioners, and funders.
Environmental stewardship is a valuable and holistic concept for guiding productive and sustained relationships with the environment. A group of colleagues and I have just published a new open access paper in the journal Environmental Management titled: “Environmental Stewardship: A conceptual review and analytical framework“. In this paper, we define local environmental stewardship as “the actions taken by individuals, groups or networks of actors, with various motivations and levels of capacity, to protect, care for or responsibly use the environment in pursuit of environmental and/or social outcomes in diverse social–ecological contexts.” We review the literature to provide a framework to guide analysis of local environmental stewardship initiatives in diverse contexts and situations.

Abstract: There has been increasing attention to and investment in local environmental stewardship in conservation and environmental management policies and programs globally. Yet environmental stewardship has not received adequate conceptual attention. Establishing a clear definition and comprehensive analytical framework could strengthen our ability to understand the factors that lead to the success or failure of environmental stewardship in different contexts and how to most effectively support and enable local efforts. Here we propose such a definition and framework. First, we define local environmental stewardship as the actions taken by individuals, groups or networks of actors, with various motivations and levels of capacity, to protect, care for or responsibly use the environment in pursuit of environmental and/or social outcomes in diverse social–ecological contexts. Next, drawing from a review of the environmental stewardship, management and governance literatures, we unpack the elements of this definition to develop an analytical framework that can facilitate research on local environmental stewardship. Finally, we discuss potential interventions and leverage points for promoting or supporting local stewardship and future applications of the framework to guide descriptive, evaluative, prescriptive or systematic analysis of environmental stewardship. Further application of this framework in diverse environmental and social contexts is recommended to refine the elements and develop insights that will guide and improve the outcomes of environmental stewardship initiatives and investments. Ultimately, our aim is to raise the profile of environmental stewardship as a valuable and holistic concept for guiding productive and sustained relationships with the environment.
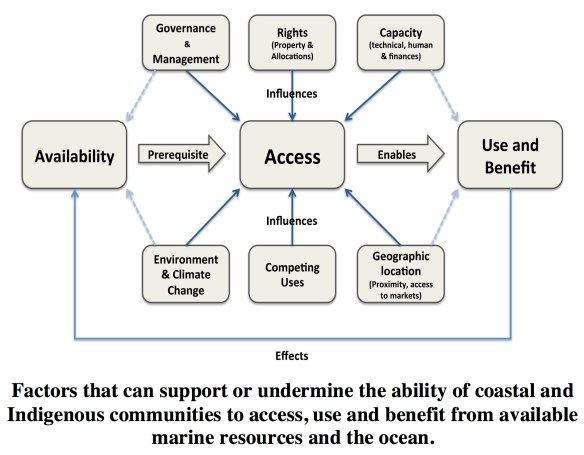
 A group representing academics, Indigenous peoples, fishers, and NGOs recently published a review and policy perspective paper in Marine Policy urging that access for coastal and Indigenous communities should be a priority consideration in all policies and decision-making processes related to fisheries and the ocean in Canada. The ability to use and benefit from marine resources (including fisheries) and areas of the ocean or coast is central to the sustainability of coastal communities. In Canada, however, access to marine resources and spaces is a significant and growing issue for many coastal and Indigenous communities due to an increasingly busy ocean: ocean-related development, competition over fisheries and marine resources, and marine planning and conservation activities that confine activities to certain areas. Loss of access has implications for the well-being, including economic, social, cultural, health, and political considerations, and persistence of coastal and Indigenous communities across the Pacific, Atlantic and Arctic coasts of Canada. The vibrancy and continuity of these communities is important to Canadian society for many reasons, including identity, autonomy, sovereignty, culture, healthy rural-urban dynamics, and environmental sustainability. Greater attention is needed to the various factors that support or undermine the ability of coastal and Indigenous communities to access and benefit from the ocean and how to reverse the current trend to ensure that coastal and Indigenous communities thrive in the future.
A group representing academics, Indigenous peoples, fishers, and NGOs recently published a review and policy perspective paper in Marine Policy urging that access for coastal and Indigenous communities should be a priority consideration in all policies and decision-making processes related to fisheries and the ocean in Canada. The ability to use and benefit from marine resources (including fisheries) and areas of the ocean or coast is central to the sustainability of coastal communities. In Canada, however, access to marine resources and spaces is a significant and growing issue for many coastal and Indigenous communities due to an increasingly busy ocean: ocean-related development, competition over fisheries and marine resources, and marine planning and conservation activities that confine activities to certain areas. Loss of access has implications for the well-being, including economic, social, cultural, health, and political considerations, and persistence of coastal and Indigenous communities across the Pacific, Atlantic and Arctic coasts of Canada. The vibrancy and continuity of these communities is important to Canadian society for many reasons, including identity, autonomy, sovereignty, culture, healthy rural-urban dynamics, and environmental sustainability. Greater attention is needed to the various factors that support or undermine the ability of coastal and Indigenous communities to access and benefit from the ocean and how to reverse the current trend to ensure that coastal and Indigenous communities thrive in the future.
|
KEY MESSAGES Access to marine resources and the ocean is important for the well-being of coastal populations. In Canada, the ability of many coastal and Indigenous communities to access and benefit from the ocean is a growing issue. Access for coastal and Indigenous communities should be a priority consideration in all policies and decision-making processes related to fisheries and the ocean in Canada. Taking action now could reverse the current trend and ensure that coastal and Indigenous communities thrive in the future. |
Recommended actions include:
|
**For more information, refer to the following publication and policy brief: Bennett NJ et al. 2018. Coastal and Indigenous community access to marine resources and the ocean: A policy imperative for Canada. Marine Policy 87:186–193. Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308597X17306413 Policy Brief: Maintaining coastal and Indigenous community access to marine resources and the ocean in Canada |
This work was supported by the OceanCanada Partnership through a grant from the Social Science and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) of Canada. For more information, please email myself (nathan.bennett@ubc.ca) or Megan Bailey (megan.bailey@dal.ca).

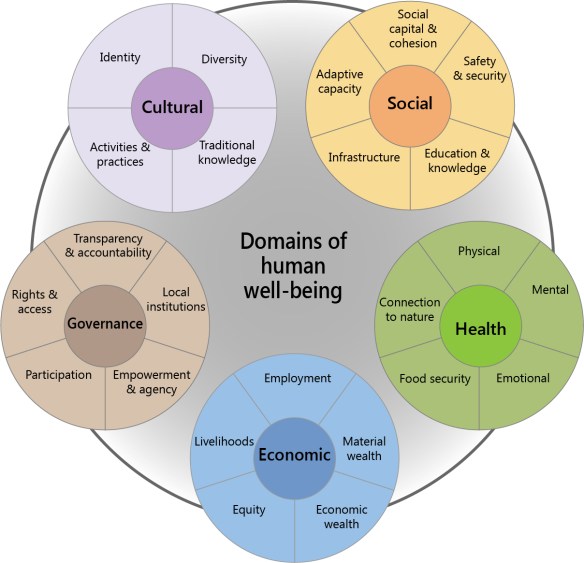
Concerns about the negative consequences of conservation for local people have prompted attention toward how to address the social impacts of different conservation projects, programs, and policies. Inevitably, when actions are taken to protect or manage the environment this will produce a suite of both positive and negative social impacts for local communities and resource users. Thus, a challenge for conservation and environmental decision-makers and managers is maximizing social benefits while minimizing negative burdens across social, economic, cultural, health, and governance spheres of human well-being. The last decade has seen significant advances in both the methods and the metrics for understanding how conservation and environmental management impact human well-being. There has also been increased uptake in socio-economic monitoring programs in conservation organizations and environmental agencies. Yet, little guidance exists on how to integrate the results of social impact monitoring back into conservation management and decision-making. We recommend that conservation organizations and environmental agencies take steps to better understand and address the social impacts of conservation and environmental management. This can be achieved by integrating key components of the adaptive social impact management (ASIM) cycle outlined below, and in a new paper published today in Conservation Biology, into decision-making and management processes**.
Conservation and environmental management can have positive or negative impacts on the well-being of local communities.
|
Take away messages: Conservation and environmental management can produce both positive and negative social impacts for local communities and resource users. Thus it is necessary to understand and adaptively manage the social impacts of conservation over time. This will improve social outcomes, engender local support and increase the overall effectiveness of conservation. |
Adaptive social impact management
Adaptive social impact management (ASIM) is “the ongoing and cyclical process of monitoring and adaptively managing the social impacts of an initiative through the following four stages: profiling, learning, planning and implementing.”

The cycle of adaptive social impact management for conservation and environmental management.
For more information, please refer to:
Contacts: Please email Maery Kaplan-Hallam (maerykaplan@gmail.com) or Dr. Nathan Bennett (nathan.bennett@ubc.ca).
In a paper recently published in Fish & Fisheries, we question whether the “Malthusian overpopulation narrative” alone is an adequate explanation for overfishing and for designing responses. Our review, led by Dr Elena Finkbeiner of the Center for Ocean Solutions at Stanford University, suggests that there is a need to better engage with the factors that mediate the relationship between population and overfishing. These mediating drivers include technology and innovation, demand and distribution, marginalization and equity, and governance and management. Accurate diagnosis of the causes of the overfishing will lead to the design of more effective and more equitable management responses.
Reference: Finkbeiner, E., N. Bennett, T. Frawley, C. Brooks, J. Mason, Ng, C., Ourens, R., Seto, K., Swanson, S., Urteaga, J., Wingfield, D. & Crowder, L.B. (2017). Reconstructing overfishing: Moving beyond Malthus for equitable and effective solutions. Fish & Fisheries. Online.
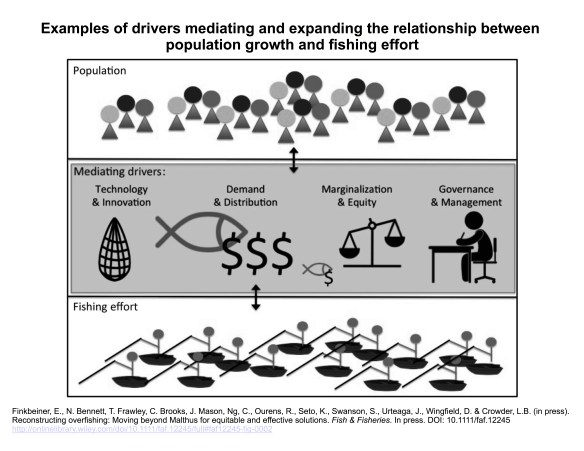
Examples of drivers mediating the relationship between population growth and fishing effort. (Source: Finkbeiner et al (2017). Reconstructing overfishing: Moving beyond Malthus for effective and effective solutions, Fish & Fisheries, DOI: 10.1111/faf.12245)
Abstract: Inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis of the root causes of overfishing can lead to misguided and ineffective fisheries policies and programmes. The “Malthusian overfishing narrative” suggests that overfishing is driven by too many fishers chasing too few fish and that fishing effort grows proportionately to human population growth, requiring policy interventions that reduce fisher access, the number of fishers, or the human population. By neglecting other drivers of overfishing that may be more directly related to fishing pressure and provide more tangible policy levers for achieving fisheries sustainability, Malthusian overfishing relegates blame to regions of the world with high population growth rates, while consumers, corporations and political systems responsible for these other mediating drivers remain unexamined. While social–ecological systems literature has provided alternatives to the Malthusian paradigm, its focus on institutions and organized social units often fails to address fundamental issues of power and politics that have inhibited the design and implementation of effective fisheries policy. Here, we apply a political ecology lens to unpack Malthusian overfishing and, relying upon insights derived from the social sciences, reconstruct the narrative incorporating four exemplar mediating drivers: technology and innovation, resource demand and distribution, marginalization and equity, and governance and management. We argue that a more nuanced understanding of such factors will lead to effective and equitable fisheries policies and programmes, by identifying a suite of policy levers designed to address the root causes of overfishing in diverse contexts.
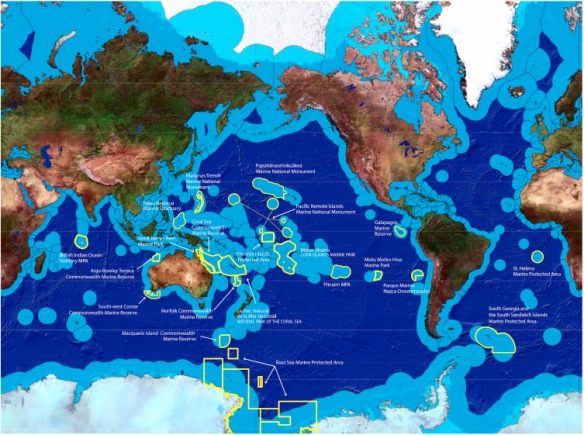
Large-scale marine protected areas in 2016-2017 (Source: Big Ocean)
More than two years ago, I took up a Fulbright Visiting Scholar position in the School of Marine and Environmental Affairs at the University of Washington with Dr. Patrick Christie. Along with a team of collaborators from academic institutions and conservation organizations, we began the lengthy process of applying for funding and then co-organizing a global “Think Thank on the Human Dimensions of Large Scale Marine Protected Areas”. The meeting, which took place in February 2016 in Honolulu, Hawaii, was attended by more than 125 scholars, practitioners, traditional leaders, managers, funders and government representatives from around the world. Through facilitating a dialogue with all participants, we aimed to co-produce knowledge at a global scale about how human dimensions considerations might be incorporated into the planning and ongoing management of large scale marine protected areas. The think tank led to a “A Practical Framework for Addressing the Human Dimensions of Large-Scale Marine Protected Areas” and a subsequent academic article (link – see abstract below). This engagement and process demonstrates the benefits of global collaborations and how knowledge co-production processes can lead to the development of both practical and academic insights on global environmental challenges.

Participants of the Think Tank on the Human Dimensions of Large-Scale Marine Protected Areas
Christie, P. Bennett, N. J., Gray, N., Wilhelm, A., Lewis, N., Parks, J., Ban, N., Gruby, R., Gordon, L., Day, J., Taei, S. & Friedlander, A. (2017). Why people matter in ocean governance: Incorporating human dimensions into large-scale marine protected areas. Marine Policy, 84, 273-284. (link)
Abstract: Large-scale marine protected areas (LSMPAs) are rapidly increasing. Due to their sheer size, complex socio-political realities, and distinct local cultural perspectives and economic needs, implementing and managing LSMPAs successfully creates a number of human dimensions challenges. It is timely and important to explore the human dimensions of LSMPAs. This paper draws on the results of a global “Think Tank on the Human Dimensions of Large Scale Marine Protected Areas” involving 125 people from 17 countries, including representatives from government agencies, non-governmental organizations, academia, professionals, industry, cultural/indigenous leaders and LSMPA site managers. The overarching goal of this effort was to be proactive in understanding the issues and developing best management practices and a research agenda that address the human dimensions of LSMPAs. Identified best management practices for the human dimensions of LSMPAs included: integration of culture and traditions, effective public and stakeholder engagement, maintenance of livelihoods and wellbeing, promotion of economic sustainability, conflict management and resolution, transparency and matching institutions, legitimate and appropriate governance, and social justice and empowerment. A shared human dimensions research agenda was developed that included priority topics under the themes of scoping human dimensions, governance, politics, social and economic outcomes, and culture and tradition. The authors discuss future directions in researching and incorporating human dimensions into LSMPAs design and management, reflect on this global effort to co-produce knowledge and re-orient practice on the human dimensions of LSMPAs, and invite others to join a nascent community of practice on the human dimensions of large-scale marine conservation.
Coastal communities are struggling with the complex social and ecological impacts of a growing global hunger for a seafood delicacy, according to a new study from the University of British Columbia.
“Soaring demand has spurred sea cucumber booms across the globe,” says lead author Mary Kaplan-Hallam, who conducted the research as a master’s student with the Institute for Resources, Environment and Sustainability (IRES) at UBC.
“For many coastal communities, sea cucumber isn’t something that was harvested in the past. Fisheries emerged rapidly. Money, buyers and fishers from outside the community flooded in. This has also increased pressure on other already overfished resources.”
Sea cucumber can sell for hundreds–sometimes thousands–of dollars a pound. The “gold rush” style impacts of high-value fisheries exacerbate longer-term trends in already vulnerable communities, such as declines in traditional fish stocks, population increases, climate change and illegal fishing.
“These boom-and-bust cycles occur across a range of resource industries,” says co-author Nathan Bennett, a postdoctoral fellow at UBC. “What makes these fisheries so tricky is that they appear rapidly and often deplete local resources just as rapidly, leaving communities with little time to recover.”

Sea cucumber fishing season 2016 (Dzilam de Bravo, Yucatan, Mexico). Credit: Eva Coronado, National Polytechnic Institute, Mexico.
The researchers based their findings on a case study of Río Lagartos, a fishing community on Mexico’s Yucatán Peninsula. For the past 50 years, small-scale commercial fishing has been the dominant livelihood of the community.
The town’s first commercial sea cucumber permits were issued in 2013, a significant economic opportunity for fishers in the region. The leathery marine animals are a delicacy in many parts of Asia, and as stocks have depleted there, demand has rapidly depleted fisheries across the globe.
A host of new challenges emerged in Río Lagartos as the sea cucumbers attracted outside fishers, money and patrons, according to the researchers’ interviews with community members.
“Resource management, incomes, fisher health and safety, levels of social conflict and social cohesion in the community are all impacted,” says Kaplan-Hallam. “The potential financial rewards are also causing local fishers to take bigger risks as sea cucumber stocks are depleted and diving must occur further from shore, with dire health consequences.”
Unfortunately, say the authors, this isn’t an isolated situation.
“There are many examples around the world where elite global seafood markets–abalone, sea urchins, sharks–are undermining local sustainability,” says Bennett. “If we want to sustainably manage fisheries with coastal communities, we need a better understanding of how global seafood markets impact communities and how to manage these impacts quickly. Think of it like an epidemic: it requires a rapid response before it gets out of control.”
###
The study “Catching sea cucumber fever in coastal communities” is published in Global Environmental Change
The research was funded by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, MITACS, the Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship program, and the Liber Ero Fellowship program.

Migrant workers on a fishing boat on the Andaman coast of Thailand (Photo: Nathan Bennett)
Five years ago when working on several projects with the UN FAO’s Bay of Bengal Large Marine Ecosystem Project in Southeast Asia, I became aware of how the global seafood industry was rife with social issues (report). These issues included slavery, welfare and safety issues, child labor, inequitable access to resources for coastal communities, lack of consideration of small-scale fishers in decision-making and ocean grabbing.
Over the past year, I was part of a working group that examined how the global seafood industry might commit to sourcing more socially responsible seafood. This initiative led to a first paper published in Science titled “Committing to socially responsible seafood“. This is just the first step in a much longer initiative.
Summary: Seafood is the world’s most internationally traded food commodity. Approximately three out of every seven people globally rely on seafood as a primary source of animal protein (1). Revelations about slavery and labor rights abuses in fisheries have sparked outrage and shifted the conversation (2, 3), placing social issues at the forefront of a sector that has spent decades working to improve environmental sustainability. In response, businesses are seeking to reduce unethical practices and reputational risks in their supply chains. Governments are formulating policy responses, and nonprofit and philanthropic organizations are deploying resources and expertise to address critical social issues. Yet the scientific community has not kept pace with concerns for social issues in the sector. As the United Nations Ocean Conference convenes in New York (5 to 9 June), we propose a framework for social responsibility and identify key steps the scientific community must take to inform policy and practice for this global challenge. More…
Link to paper: Committing to socially responsible seafood
Eureka Alert News Release: Scientists launch global agenda to curb social, human rights abuses in seafood sector

A group of colleagues and I have just published an open access paper titled “An appeal for a code of conduct for marine conservation” in Marine Policy. In this paper, we propose that:
Abstract: Marine conservation actions are promoted to conserve natural values and support human wellbeing. Yet the quality of governance processes and the social consequences of some marine conservation initiatives have been the subject of critique and even human rights complaints. These types of governance and social issues may jeopardize the legitimacy of, support for and long-term effectiveness of marine conservation. Thus, we argue that a clearly articulated and comprehensive set of social standards – a code of conduct – is needed to guide marine conservation. In this paper, we draw on the results of an expert meeting and scoping review to present key principles that might be taken into account in a code of conduct, to propose a draft set of foundational elements for inclusion in a code of conduct, to discuss the benefits and challenges of such a document, and to propose next steps to develop and facilitate the uptake of a broadly applicable code of conduct within the marine conservation community. The objectives of developing such a code of conduct are to promote fair conservation governance and decision-making, socially just conservation actions and outcomes, and accountable conservation practitioners and organizations. The uptake and implementation of a code of conduct would enable marine conservation to be both socially acceptable and ecologically effective, thereby contributing to a truly sustainable ocean.
Press releases and coverage
Policy Brief: An appeal for a code of conduct for marine conservation (PDF LINK)
Reference: Bennett, N.J., Teh, L., Ota, Y., Christie, P., Ayers, A., Day, J.C., Franks, P., Gill, D., Gruby, R.L., Kittinger, J.N., Koehn, J.Z., Lewis, N., Parks, J., Vierros, M., Whitty, T.S., Wilhelm, A., Wright, K., Aburto, J.A., Finkbeiner, E.M., Gaymer, C.F., Govan, H., Gray, N., Jarvis, R.M., Kaplan-Hallam, M. & Satterfield, T. (2017). An appeal for a code of conduct for marine conservation. Marine Policy, 81, 411–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2017.03.035 [OPEN ACCESS]